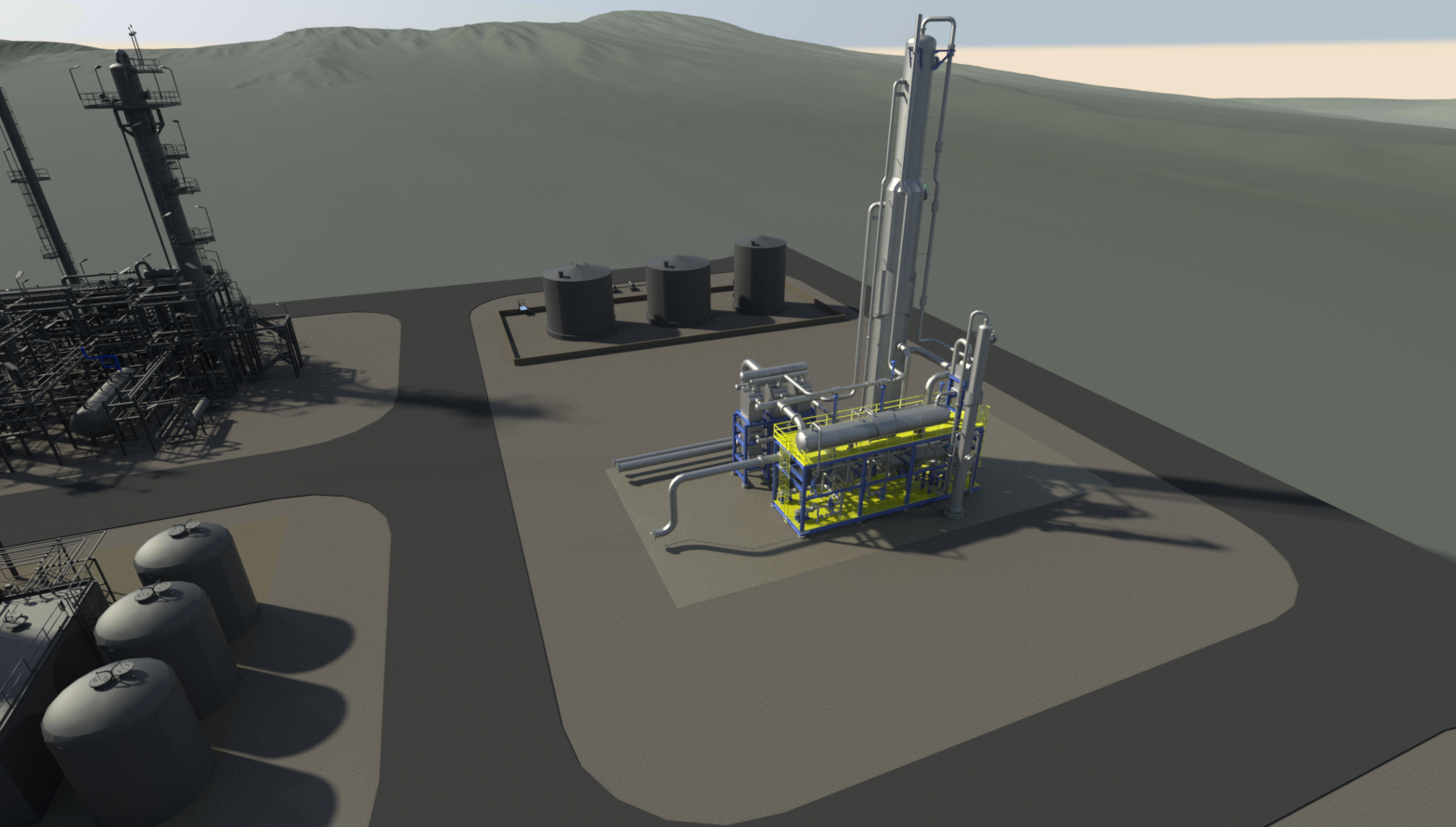
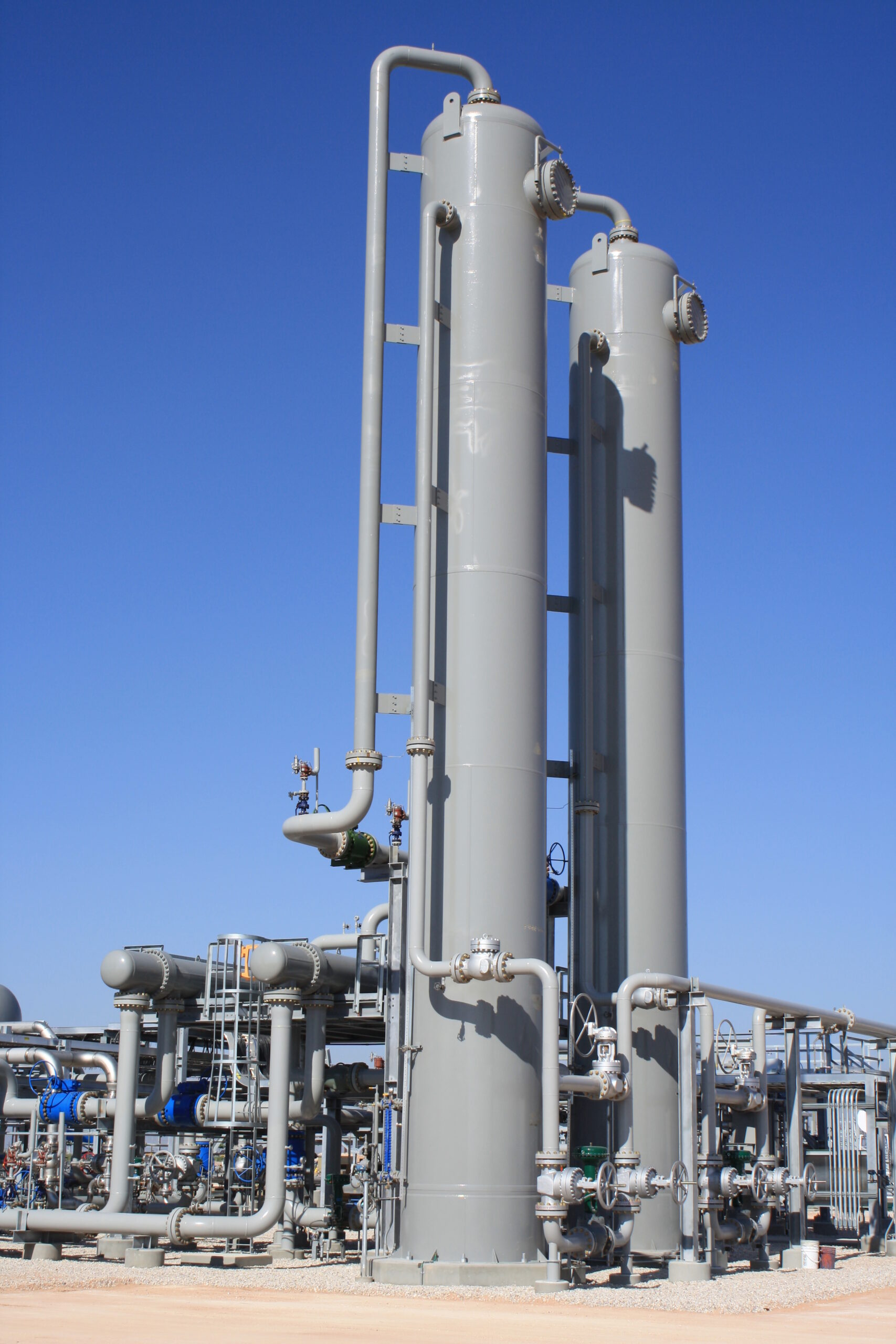
Optimizing Amine Treating for Maximum Efficiency
The world of amine treating is a critical part of the petroleum and natural gas industries. It’s an essential process that removes acidic gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from natural gas and refinery streams. However, designing an effective amine plant can be challenging. From material selection to heater design, various factors can influence the efficiency and success of the operation. In this post, we’ll explore best practices in amine treating to help you overcome common pitfalls and achieve optimal results.
Understanding Amine Treating Basics
Amine treating, also known as gas sweetening, involves using aqueous solutions of amines to absorb acidic gases. This process is crucial as it prevents corrosion in pipelines and equipment, ensuring the safe transport of gas. Amine treating uses different types of amines, including monoethanolamine (MEA), diethanolamine (DEA), and methyldiethanolamine (MDEA), or other specialty amines each with unique properties suited for specific applications.
A key aspect of amine treating is rich loading, which refers to the amount of acid gas absorbed by the amine solution. Designing your plant with an acceptable rich loading is vital for efficient operation. Overloading can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased corrosion risks, while underloading may result in wasted resources.
Designing for Solvent Dependency
The choice of amine solvent significantly impacts the amine treating process. Each solvent has unique characteristics that dictate its suitability for specific applications. Factors like acid gas concentration, pressure, temperature, and the presence of impurities must be considered when selecting the right solvent.
It’s essential to design your plant with solvent dependency in mind. This means accounting for the specific properties of your chosen amine and adapting your process accordingly. By doing so, you can ensure that your plant operates efficiently and effectively, maximizing the absorption of acidic gases.
Ensuring Sufficient Heat for Regeneration
Regeneration is a critical step in amine treating, where absorbed acidic gases are stripped from the amine solution, allowing it to be reused. Adequate heat is crucial for this process, as it drives the desorption of gases. Insufficient heat can lead to incomplete regeneration, reducing the efficiency of your plant.
To avoid this, ensure that you have enough heat available, usually above the minimums provided by solvent vendors. By designing your system with ample heating capacity, you can facilitate efficient regeneration and maintain high plant performance.
Optimizing Vessel Internals
Vessel internals play a crucial role in the amine treating process. They influence the flow, pressure, temperature, and composition of the gas and liquid streams. Choosing the right type of internals, such as valve trays or packing, is essential for optimizing your plant’s performance.
It’s important to design your vessel internals to support multiple design scenarios. This means considering variations in inlet conditions and ensuring that your internals can handle these changes. By doing so, you’ll create a more adaptable and efficient system.
Addressing Heater Design and Fuel Train
Heaters are often a weak point in amine plants, with design flaws leading to operational failures. A conservative heat flux and sufficient hot oil flow are essential design considerations for heaters. Additionally, ensure that the refractory is correctly installed, and the coil is fully tested for leaks.
By focusing on these aspects of heater design, you’ll reduce the likelihood of failures and improve the overall efficiency of your amine plant. This attention to detail will help maintain consistent performance and prevent costly downtime.
Selecting Appropriate Materials of Construction
Material selection is a critical aspect of amine treating, as different materials are required at various stages of the process. Stainless steel (SS) is often used for internals with no corrosion allowance, as it offers excellent resistance to the corrosive nature of acidic gases.
High corrosion areas, such as the rich, two-phase amine and reflux system, require careful material selection to ensure durability. Consider the composition of the feed, as the presence of H2S can help delay corrosion by creating a passivating layer. By choosing the right materials, you’ll extend the lifespan of your equipment and improve plant reliability.
Managing Corrosion Tendencies
Corrosion is a significant concern in amine treating, as it can lead to equipment failure and costly repairs. Understanding corrosion tendencies and taking proactive measures can help mitigate these risks. Composition-dependent factors, such as the presence of H2S, can influence corrosion rates and should be considered when designing your plant.
Implementing regular maintenance and monitoring programs can help identify potential corrosion issues early, allowing you to address them before they become major problems. By staying vigilant, you’ll ensure the longevity and efficiency of your amine treating operations.
In summary, optimizing amine treating for maximum efficiency involves careful consideration of various factors, from solvent selection to material choice. By following best practices and addressing common pitfalls, you’ll create a more reliable and effective plant. These strategies will not only improve operational performance but also contribute to the safety and sustainability of your gas processing operations.
To explore more about amine treating best practices and enhance your plant’s efficiency, consider consulting with industry experts or accessing additional resources. By continually expanding your knowledge and staying informed, you’ll empower your organization to excel in this critical aspect of the petroleum and natural gas industries.
Plan an introduction meeting today
Contact our experts today to discover how our innovative solutions can tackle your complex energy challenges